Platelet Indices in Acute Myocardial Infarction - An Observational Study
Authors
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.main##
Abstract
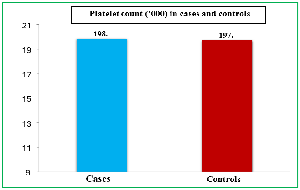
Background: Platelet volume indices (PVI) such as mean platelet volume (MPV), platelet distribution width (PDW), and plateletcrit (PCT) have been implicated in the pathogenesis and prognosis of acute coronary syndromes (ACS). This study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic and prognostic utility of PVI in ACS among the Kashmiri population. Methods: A prospective observational study was conducted at GMC Srinagar from October 2022 to April 2024, enrolling 570 ACS patients and 285 age- and sex-matched healthy controls. PVI were compared between cases and controls, as well as among ACS subtypes: STEMI, NSTEMI, and unstable angina. Prognostic value was assessed for in-hospital and 30-day mortality. Results: MPV, PDW, and PCT were significantly higher in ACS patients compared to controls (p<0.001 for all). STEMI patients had significantly higher MPV and PDW compared to NSTEMI and unstable angina groups. PCT did not differ significantly among ACS subtypes. Multivariate analysis identified age ≥60 years, STEMI presentation, and elevated PDW as independent predictors of 30-day mortality. Platelet count did not differ significantly between cases and controls or among ACS subtypes. Conclusion: Elevated MPV, PDW, and PCT are associated with ACS and can be measured easily through routine hematological analysis. PDW, in particular, has prognostic significance for short-term mortality. PVI offer a simple, cost-effective adjunct for early detection, risk stratification, and prognostication in ACS.
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.details##
Copyright (c) 2025 Dr Mustafa Bashir, Dr Tavseef Ahmad Tali, Ms Bilkees Ashraf, Dr Toufeeq Ahmed Teli, Dr Fiza Amin

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Creative Commons License All articles published in Annals of Medicine and Medical Sciences are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Dr Mustafa Bashir, Department of General Medicine, Government Medical College Baramulla, J&K, India.
Department of General Medicine, Government Medical College Baramulla, J&K, India.
Dr Tavseef Ahmad Tali, Department of Radiation Oncology, Government Medical College Baramulla, J&K, India.
Department of Radiation Oncology, Government Medical College Baramulla, J&K, India.
Ms Bilkees Ashraf, Community Health Officer, Block Zachaldara Handwara Kupwara, J&K, India.
Community Health Officer, Block Zachaldara Handwara Kupwara, J&K, India.
Dr Toufeeq Ahmed Teli, Department of General Medicine, Government Medical College Udhampur, J&K, India.
Department of General Medicine, Government Medical College Udhampur, J&K, India.
Dr Fiza Amin, Department of Gynaecology & Obstetrics, Ramzaan Hospital Gogji Bagh, Srinagar, J&K, India.
Department of Gynaecology & Obstetrics, Ramzaan Hospital Gogji Bagh, Srinagar, J&K, India.
[1] Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, et al. Third universal definition of myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 2012;60:1581-98.
[2] Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, et al. Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction (2018). Circulation 2018; 138: e618-51.
[3] Murray CJ, Barber RM, Foreman KJ, et al. Global, regional, and national disability adjusted life years (DALYs) for 306 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 188 countries, 1990- 2013: quantifying the epidemiological transition. Lancet 2015; 386: 2145-91.
[4] Gupta R, Mohan I, Narula J. Trends in Coronary Heart Disease Epidemiology in India. Annals of Global Health. 2016;82:307-15.
[5] Prabhakaran D, Jeemon P, Roy A. Cardiovascular Diseases in India. Current Epidemiology and Future Directions. Circulation.2016;133:1605-20.
[6] Roffi M, Patrono C, Collet JP, Mueller C, Valgimigli M, Andreotti F, Bax JJ, Borger MA, Brotons C, Chew DP, Gencer B, Hasenfuss G, Kjeldsen K, Lancellotti P, Landmesser U, Mehilli J, Mukherjee D, Storey RF, Windecker S, ESC Scientific Document Group. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation: Task Force for the Management of Acute Coronary Syndromes in Patients Presenting without Persistent ST-Segment Elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 2016; 37:267_315.
[7] Ibanez B, James S, Agewall S, Antunes MJ, Bucciarelli-Ducci C, Bueno H, Caforio ALP, Crea F, Goudevenos JA, Halvorsen S, Hindricks G, Kastrati A, Lenzen MJ, Prescott E, Roffi M, Valgimigli M, Varenhorst C, Vranckx P, Widimsky P, ESC Scientific Document Group. 2017 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation: The Task Force for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST segment elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 2018;39:119_177.
[8] Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, Chaitman BR, Bax JJ, Morrow DA, White HD, ESC Scientific Document Group. Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction (2018). Eur Heart J 2019;40:237_269. Investigators. Effect of definition on incidence and prognosis of type 2 myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 2017;70:1558_1568.
[9] Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, et al. Third universal definition of myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 2012;60: 1581-98.
[10] Murray CJ, Barber RM, Foreman KJ, et al. Global, regional, and national disability- adjusted life years (DALYs) for 306 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 188 countries, 1990- 2013: quantifying the epidemiological transition. Lancet 2015; 386:2145-91.
[11] Libby P. Mechanisms of acute coro- nary syndromes and their implications for therapy. N Engl J Med 2013; 368:2004- 13.
[12] O’Gara PT, Kushner FG, Ascheim DD, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of ST-elevation myocardial infarction: areport of the American Col lege of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol 2013;61(4): e78-e140.
[13] Amsterdam EA, Wenger NK, Brindis RG, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with non-ST-ele- vation acute coronary syndromes: a report of the American College of Cardiology/ American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol 2014;64(24):e139-e228.
[14] Savonitto S, Ardissino D, Granger CB, et al. Prognostic value of the admission electrocardiogram in acute coronary syndromes. JAMA 1999; 281:707-13.
[15] Welch RD, Zalenski RJ, Frederick PD, et al. Prognostic value of a normal or nonspecific initial electrocardiogram in acute myocardial infarction. JAMA 2001;286:1977- 84.
[16] Cannon CP, McCabe CH, Stone PH, et al. The electrocardiogram predicts one-year outcome of patients with unstable angina andnon-Q wave myocardial infarction: results of the TIMI III Registry ECG Ancillary Study. Thrombolysis in Myocardial Ischemia. J Am Coll Cardiol 1997; 30:133- 40.
[17] Westerhout CM, Fu Y, Lauer MS, et al. Short- and long-term risk stratification in acute coronary syndromes: the added value of quantitative ST-segment depression and multiple biomarkers. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006;48:939-47.
[18] Heeschen C, Hamm CW, Bruemmer J, Simoons ML. Predictive value of C reactive protein and troponin T in patients with unstable angina: a comparative analysis. CAPTURE Investigators. Chimeric c7E3 Anti Platelet Therapy in Unstable angina Refractory to standard treatment trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 2000;35:1535- 42.
[19] Heidenreich PA, Alloggiamento T, Melsop K, McDonald KM, Go AS, Hlatky MA. The prognostic value of troponin in patients with non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome: a meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 2001; 38:478-85.
[20] James SK, Lindbäck J, Tilly J, et al. Troponin-T and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide predict mortality benefit from coronary revascularization in acute coronary syndromes: a GUSTO-IV substudy. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006; 48:1146-54.
[21] Giannitsis E, Muller-Bardorff M, Lehrke S, et al. Admission troponin T level predicts clinical outcomes, TIMI flow, and myocardial tissue perfusion after primary percutaneous intervention for acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Circulation 2001;104: 630-5.
[22] Ohman EM, Armstrong PW, Christenson RH, et al. Cardiac troponin T levels for risk stratification in acute myocardial ischemia. GUSTO IIA Investigators. N Engl J Med1996; 335:1333-41.
[23] Panteghini M, Cuccia C, Bonetti G, Giubbini R, Pagani F, Bonini E. Single-point cardiac troponin T at coronary care unit discharge after myocardial infarction correlates with infarct size and ejection fraction. Clin Chem 2002; 48:1432-6.
[24] de Lemos JA, Morrow DA, Bentley JH, et al. The prognostic value of B-type natriuretic peptide in patients with acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med 2001; 345:1014-21.
[25] James SK, Lindahl B, Siegbahn A, et al. N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide and other risk markers for the separate prediction of mortality and subsequent myocardial infarction in patients with unstable coronary artery disease: a Global Utilization of Strategies to Open occluded arteries (GUSTO)-IV substudy. Circulation 2003; 108:275-81.
[26] Mega JL, Morrow DA, De Lemos JA, et al. B-type natriuretic peptide at presentation and prognosis in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: an ENTIRE-TIMI-23 substudy. J Am Coll Cardiol 2004;44:335-9.
[27] Sabatine MS, Morrow DA, Higgins LJ, et al. Complementary roles for biomarkers of biomechanical strain ST2 and N-terminal prohormone B-type natriuretic peptide in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Circulation 2008; 117:1936 44.
[28] Anderson JL, Adams CD, Antman EM, et al. ACC/AHA 2007 guidelines for the management of patients with unstable angina/non- ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Revise the 2002 Guidelines for the Management of Patients with Unstable Angina/Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction). J Am Coll Cardiol 2007;50:e1-157.
[29] Hachamovitch R, Di Carli MF. Methods and limitations of assessing new noninvasive tests: Part II: outcomes-based validation and reliability assessment of noninvasive testing. Circulation 2008;117:2793-801.
[30] Antman EM, Anbe DT, Armstrong PW, et al. ACC/AHA guidelines for the management of patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarctionexecutive summary. A report of the American College of Cardiology/ American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to revise the 1999 guidelines for the management of patients with acute myocardial infarction). J Am Coll Cardiol 2004; 44:671-719.
[31] Kumar V, Melhotra S, Ahuja Ret RC and Viash AK. Platelet and Acute Coronary Syndrome. J Fam Med. 2016; 3(4): 1063.
[32] Jaya Manchanda, R M Potekar, Sharan Badiger, Abhishek Tiwari. The study of platelet indices in acute coronary syndromes. Annals of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Vol. 02, No. 01, Jan-Mar 2015.
[33] Singhal G, Pathak V. The relationship between mean platelet volume and coronary collateral vessels in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Journal of the Practice of Cardiovascular Sciences. 2016;2(3):169.
[34] M M Khandekar, A S Khurana, S D Deshmukh, A L Kakrani, A D Katdare, A K Inamdar Platelet volume indices in patients with coronary artery disease and acute myocardial infarction: an Indian scenario J Clin Pathol. 2006 Feb; 59(2): 146-149.
[35] Biradar SB, Kashinakunti SV, Manjula R. Platelet volume indices in acute coronary syndrome- a case control study. Int J Adv Med 2016; 3:349-52.
[36] Dehghani MR, Taghipour-Sani L, Rezaei Y, Rostami R. Diagnostic importance of admission platelet volume indices in patients with acute chest pain suggesting acute coronary syndrome. Indian Heart J 2014;66(6): 622-8.
[37] Hendra TJ, Oswald GA, Yudkin JS. Increased mean platelet volume after acute myocardial infarction relates to diabetes and to cardiac failure. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 1988; 5: 63-69.
[38] Boos CJ, Balakrishnan B, Lip GY. The effects of coronary artery disease severity on time-dependent changes in platelet activation indices in stored whole blood. J Thromb Thrombolysis 2008 ;25(2): 135-40.
[39] Cameron HA, Philips R, Ibbotson RM, Carson PHM. Platelet size in myocardial infarction. Br Med J 1983;287: 449-51.
[40] Martin JF, Plumb J, Kilbey RS, Kishk YT Changes in volume and density of platelets in myocardial infarction. Br Med J 1983;287: 456- 9.
[41] Kumar V, Melhotra S, Ahuja Ret RC and Viash AK. Platelet and Acute Coronary Syndrome. J Fam Med. 2016; 3(4): 1063.
[42] Jaya Manchanda, R M Potekar, Sharan Badiger, Abhishek Tiwari. The study of platelet indices in acute coronary syndromes. Annals of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Vol. 02, No. 01, Jan-Mar 2015.
[43] Assiri AS, Jamil AM, Mahfouz AA, Mahmoud ZS, Ghallab M. Diagnostic importance of platelet parameters in patients with acute coronary syndrome admitted to a tertiary care hospital in southwest region, Saudi Arabia. J Saudi Heart Assoc 2012;24(1): 17-21.
[44] Pervin S, Islam SM, Ferdoushi S, Hossain M, Sultana T, Hoque MH, et al. Platelet distribution width is an early indicator of acute coronary syndrome. University Heart Journal. 2013;9(1):3-8.
[45] Nandwani S, Bhatnagar M. Study of Platelet volume Indices in Platelet of Acute Coronary Events. JIAG. 2011;7:22-4.
[46] Akula, S., Krishna. K, V., J, R., Srinivas, B. and Damera, S. (2017). A Study of Platelet Indices in Acute Myocardial Infarction: An Observational Study. IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences, 16(06), pp.10-13.
[47] Khode V, Sindhur J, Kanbur D, Ruikar K, Nallulwar S. Mean platelet volume and other platelet volume indices in patients with stable coronary artery disease and acute myocardial infarction: A case control study. J Cardiovasc Dis Res 2012;3:272-5.