A Multicenter, Retrospective, Real-World Evidence Study to Evaluate the Effectiveness and Safety of Nimesulide-Paracetamol Combination Therapy for the Management of Acute Painful Conditions
Authors
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.main##
Abstract
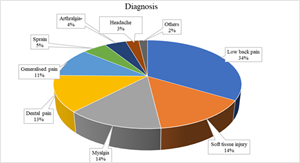
Introduction: Nimesulide-Paracetamol fixed-dose combination is widely used for managing acute painful conditions, yet real-world evidence remains limited. This study aimed to evaluate its effectiveness and safety in patients presenting with various acute painful conditions in clinical practice. Methods: This multicenter, retrospective study analyzed records of 1873 adult patients across 528 centers in India who received nimesulide-paracetamol. Pain severity was documented at baseline and follow-up (7 ± 2 days). Statistical analysis included descriptive summaries of patient characteristics and treatment outcomes. Results: Among 1873 patients (69.6% male; mean age 45.54 ± 21.22 years), common diagnoses included low back pain (33.6%), soft tissue injury (14.5%), myalgia (14.0%), and dental pain (13.2%). At baseline, 8.7% had mild pain, 34.6% moderate, and 56.7% severe pain. Following treatment, 66.8% achieved complete pain relief. Of patients with severe baseline pain (n=1062), 71.7% became pain-free, 20.2% improved to mild, 4.4% to moderate, and 3.7% remained with severe pain. Among those with moderate pain (n=648), 57.4% reported no pain after treatment. No adverse events were reported during the treatment period. Conclusion: Nimesulide-paracetamol combination therapy demonstrated substantial effectiveness and good tolerability in real-world management of acute painful conditions, achieving significant pain relief with no reported safety concerns.
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.details##
Copyright (c) 2025 Dr. Sandip Dhole, Dr. Sandeep Darbastwar, Dr. Chittanand Mendhe, Dr. Ashwini Shirbhate, Dr. Ajitkumar Gondane, Dr. Dattatray Pawar, Dr. Akhilesh Sharma

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Creative Commons License All articles published in Annals of Medicine and Medical Sciences are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Dr. Sandip Dhole, Associate Professor, PMR Department, AIIMS, Bibinagar, Telangana, India.
Associate Professor, PMR Department, AIIMS, Bibinagar, Telangana, India.
Dr. Sandeep Darbastwar, Consultant Surgeon, Galaxy Centre for Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease, Nanded, Maharashtra, India.
Consultant Surgeon, Galaxy Centre for Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease, Nanded, Maharashtra, India.
Dr. Chittanand Mendhe, Assistant Professor, Dept. of Orthopaedics, IGGMC Nagpur, Maharashtra, India.
Assistant Professor, Dept. of Orthopaedics, IGGMC Nagpur, Maharashtra, India.
Dr. Ashwini Shirbhate, Assistant Professor, VYWS Dental College & Hospital, Amravati, Maharashtra, India.
Assistant Professor, VYWS Dental College & Hospital, Amravati, Maharashtra, India.
Dr. Ajitkumar Gondane, Medical Advisor, Medical Affairs Division, Alkem Laboratories, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India.
Medical Advisor, Medical Affairs Division, Alkem Laboratories, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India.
Dr. Dattatray Pawar, Medical Lead, Medical Affairs Division, Alkem Laboratories, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India.
Medical Lead, Medical Affairs Division, Alkem Laboratories, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India.
Dr. Akhilesh Sharma, President & Chief Medical Officer, Medical Division, Alkem Laboratories, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India.
President & Chief Medical Officer, Medical Division, Alkem Laboratories, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India.
[1] Mäntyselkä P, Kumpusalo E, Ahonen R, Kumpusalo A, Kauhanen J, Viinamäki H, Halonen P, Takala J. (2001) Pain as a reason to visit the doctor: a study in Finnish primary health care. Pain;89(2-3):175-80. 10.1016/s0304-3959(00)00361-4
[2] Johnson M, Collett B, Castro-Lopes JM. (2013) The challenges of pain management in primary care: a pan-European survey. J Pain Res; 6:393-401. 10.2147/JPR.S41883
[3] Alorfi NM. (2023) Pharmacological methods of pain management: Narrative review of medication used. Int J Gen Med; 16:3247-56. 10.2147/IJGM.S419239
[4] Davison SN. (2019) Clinical Pharmacology Considerations in Pain Management in Patients with Advanced Kidney Failure. Clinical journal of the American Society of Nephrology: CJASN;14(6):917-31. 10.2215/cjn.05180418
[5] Zarghi A, Arfaei S. (2011) Selective COX-2 Inhibitors: A Review of Their Structure-Activity Relationships. Iranian journal of pharmaceutical research: IJPR;10(4):655-83.
[6] Shi S, Klotz U. (2008) Clinical use and pharmacological properties of selective COX-2 inhibitors. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology;64(3):233-52. 10.1007/s00228-007-0400-7
[7] Bindu S, Mazumder S, Bandyopadhyay U. (2020) Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and organ damage: A current perspective. Biochemical Pharmacology; 180:114147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114147
[8] Ghosh R, Alajbegovic A, Gomes AV. (2015) NSAIDs and Cardiovascular Diseases: Role of Reactive Oxygen Species. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity; 2015:536962. 10.1155/2015/536962
[9] Bennett A, Villa G. (2000) Nimesulide: an NSAID that preferentially inhibits COX-2, and has various unique pharmacological activities. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy;1(2):277-86. 10.1517/14656566.1.2.277
[10] Kress HG, Baltov A, Basiński A, Berghea F, Castellsague J, Codreanu C, Copaciu E, Giamberardino MA, Hakl M, Hrazdira L, Kokavec M, Lejčko J, Nachtnebl L, Stančík R, Švec A, Tóth T, Vlaskovska MV, Woroń J. (2016) Acute pain: a multifaceted challenge – the role of nimesulide. Current Medical Research and Opinion;32(1):23-36. 10.1185/03007995.2015.1100986
[11] Mangesh T, Muruganathan A, Dattatray P. (2022) Safety and Efficacy of Nimesulide/Paracetamol Fixed-dose Combination in Acute Pain (SAFE Study) Indian Journal of Clinical Practice;33(2):11-8.
[12] Tiwaskar M, Muruganathan A, Gondane A, Pawar D. (2023) An Open-label, Prospective, Multicentric, Cohort Study of Nimesulide/Paracetamol Fixed Drug Combination for Acute Pain Management: Sub-group Analysis. The Journal of the Association of Physicians of India;71(4):11-2. 10.5005/japi-11001-0234.
[13] Magni A, Agostoni P, Bonezzi C, Massazza G, Menè P, Savarino V, Fornasari D. Management of Osteoarthritis: Expert Opinion on NSAIDs. Pain Ther. 2021 Dec;10(2):783-808.
[14] Gondane A, Pawar D. Physician perspectives on non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: a comprehensive survey on usage and preferences.Int JBasic Clin Pharmacol 2024;13:696-701.
[15] Patil S, Nadaf N, Gupta S, et al. (April 23, 2024) A Comparative Analysis of the Efficacy and Safety of Nimesulide/Paracetamol Fixed-Dose Combination with Other NSAIDs in Acute Pain Management: A Randomized, Prospective, Multicenter, Active-Controlled Study (the SAFE-2 Study). Cureus 16(4): e58859.
[16] Tiwaskar M, Muruganathan A, Gondane A, Pawar D. An Open-label, Prospective, Multicentric, Cohort Study of Nimesulide/Paracetamol Fixed Drug Combination for Acute Pain Management: Sub-group Analysis. J Assoc Physicians India. 2023 Apr;71(4):11-12.
[17] Santos BFE, Costa FO, Vasconcelos AMA, Cyrino RM, Cota LOM. Preemptive effects of ibuprofen and nimesulide on postoperative pain control after open flap periodontal surgeries: A randomized placebo-controlled split-mouth clinical trial. J Periodontol. 2022 Feb;93(2):298-307.
[18] Umurova NM. Comparative effectiveness of nimesulide and diclofenac sodium in gout. Asian J Pharm Biol Res 2023;12(1).