Moderate Hypofractionated Irrradiation and Androgen Deprivation Therapy in Clinically Pelvic Nodes Prostate Cancer, Treatment Outcome; Single Institution Experience
Authors
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.main##
Abstract
Objectives: To test the feasibility of hypofractionated irradiation using VMAT and IGRT in non-metastatic clinically pelvic nodes prostate cancer with evaluating toxicity and survival outcomes.
Methods: Database was reviewed for all non-metastatic prostate cancer patients with initial clinical pelvic nodes between 2012 and 2017 which have received hypofractionated irradiation 50-60Gy in 20-25 fractions. All 48 patients had hormonal therapy for 24-36 months.
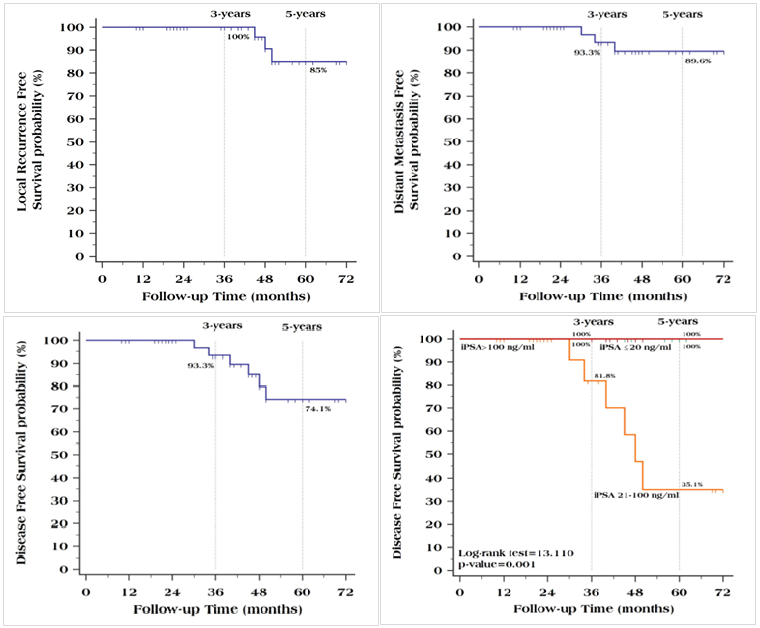
Results: With a median follow up 42 months (10-80), median age was 68 years, 50% of patients had Gleason score 7, initial PSA was between 21-100ng/ml in 56% of patients, T2 stage was in 42% of patients, 73% of patients received neoadjuvant hormonal therapy for 7-12 months, median lymph node size was 1.3cm, median PSA before irradiation was 0.6ng/ml, 45 patients received 60Gy in 25 fractions. No acute or chronic grade 3 or 4 toxicity was recorded according to RTOG toxicity scale. Local failure was in 3 patients and distant metastasis in 3 patients. Predictors of relapse were low irradiation dose (50Gy had 100% relapse vs. 6.7% of 60Gy [P=0.001]) and initial PSA which had marginally significant effect (P=0.069). Initial PSA >100ng/ml and irradiation dose had significant effect on Disease Free Survival (P=0.001 & < 0.001 respectively). Local Recurrence Free Survival was 100%, 85% and 85% at 3, 5 and 6 years respectively. Distant Metastasis Free Survival was 93.3%, 89.6% and 89.6% at 3, 5 and 6 years respectively. DFS was 93.3%, 74.1% and 74.1% at 3, 5 and 6 years respectively. All patients were a live at last follow up visits.
Conclusion: The moderate hypofractionated radiotherapy regimen is well tolerated in this cohort of clinically pelvic nodes prostate cancer patients. The patients who received higher dose of 60Gy in 25 fractions had better outcomes. We propose further dose escalation with modern radiotherapy techniques.
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.details##
Copyright (c) 2022 MW Hegazy, M. Rizwanullah

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Creative Commons License All articles published in Annals of Medicine and Medical Sciences are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.