Wired for Success or Plated for Perfection?: A Comparative Study of Distal Radius Fracture Fixation
Authors
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.main##
Abstract
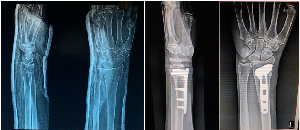
Background: Distal radius fractures are the most frequent fractures, with a common cause being low-energy falls. Treatment is focused on restoring anatomical alignment, stability, and functional results. Two very common surgical modalities employed are Kirschner (K-wire) fixation and Open Reduction Internal Fixation (ORIF) with plating. Aim and Objective: The aim of this study is to compare the outcomes and effectiveness of K-wire fixation versus ORIF plating in treating distal radius fractures. Material and Methods: Retrospective comparative study was performed on those patients with distal radius fracture who were operated with either K-wire fixation or ORIF plating. Data collected from records of patients from a tertiary care centre. Results: The gender distribution (P-value=0.765) and side of fracture (P-value=1.000) are statistically insignificant between the ORIF and K-wire groups. Fracture type distribution is not statistically significant between the two groups (P-value=0.128), although K-wire was not used any cases of 2R3C fractures. The average age in the ORIF group was also lower (40.5 years) than that of the K-wire group (47.5 years), and not statistically significant (P-value=0.090). The ORIF group's average post-operative blood loss (60.0 ml) was significantly higher than the K-wire group's (12.5 ml), and with statistical significance (P-value=0.000). The mean operation time was much longer in the ORIF group (105.0 min) than in the K-wire group (75.0 min), and the difference was statistically significant (P-value0.000). 3 patients (20.0%) had superficial infection in the K-wire group, but none in the ORIF group. The difference was statistically significant (P-value=0.017). Conclusion: K-wire fixation and ORIF plating yield satisfactory outcomes in distal radius fractures, ORIF plating may offer superior early functional recovery and better maintenance of anatomical reduction in certain fracture patterns, albeit with potentially higher cost. K-wire fixation remains a viable and cost-effective option for simpler fracture configurations with comparable long-term results.
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.details##
Copyright (c) 2025 Vinay Kumar, Sajjad Ali, Mohammed Irshad PM, Dibin DK

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Creative Commons License All articles published in Annals of Medicine and Medical Sciences are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
[1] Court-Brown CM, Caesar B. Epidemiology of adult fractures: A review. Injury. 2006;37(8):691-697. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2006.04.130
[2] Mehta SP, Karagiannopoulos C, Pepin ME, et al. Distal Radius Fracture Rehabilitation. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2024;54(9): CPG1-CPG78. doi:10.2519/jospt.2024.0301
[3] Wang R, Wu L, Wang Y, et al. Limited Open Reduction and Transepiphyseal Intramedullary Kirschner Wire Fixation for Treatment of Irreducible Distal Radius Diaphyseal Metaphyseal Junction Fracture in Older Children. Front Pediatr. 2022;10:871044. Published 2022 Apr 13. doi:10.3389/fped.2022.871044
[4] Di Giacinto S, Pica G, Stasi A, et al. The challenge of the surgical treatment of paediatric distal radius/ forearm fracture: K wire vs plate fixation - outcomes assessment. Med Glas (Zenica). 2021;18(1):208-215. doi:10.17392/1315-21
[5] Mirarchi AJ, Nazir OF. Minimally Invasive Surgery: Is There a Role in Distal Radius Fracture Management?. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2021;14(1):95-100. doi:10.1007/s12178-020-09689-x
[6] Bachoura A, Shin EK. Emerging Technologies in Distal Radius Fracture Fixation. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. Published online June 22, 2019. doi:10.1007/s12178-019-09568-0
[7] Doermann A, Gupta DK, Wright DJ, et al. Distal Radius Fracture Management: Surgeon Factors Markedly Influence Decision Making. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2023;7(3):e23.00002. Published 2023 Mar 2. doi:10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-23-00002.
[8] Heifner JJ, Halpern AL, Wahood M, Mercer DM, Orbay JL. Acute on Chronic Distal Radius Fracture: A Case Series and Technique Description. J Hand Surg Glob Online. 2022;4(6):328-331. Published 2022 Sep 16. doi:10.1016/j.jhsg.2022.08.009
[9] Meaike JJ, Kakar S. Management of Comminuted Distal Radius Fractures: A Critical Analysis Review. JBJS Rev. 2020;8(8):e2000010. doi:10.2106/JBJS.RVW.20.00010
[10] Ermutlu C, Mert M, Kovalak E, Kanay E, Obut A, Öztürkmen Y. Management of Distal Radius Fractures: Comparison of Three Methods. Cureus. 2020;12(8):e9875. Published 2020 Aug 19. doi:10.7759/cureus.9875
[11] Awasthi A, Jadhav S, Taywade S, Salwan A, Khan K. Outcome Analysis of Distal End Radius Fractures Managed with Antegrade Intramedullary K-wire Fixation. Cureus. 2022;14(10):e30512. Published 2022 Oct 20. doi:10.7759/cureus.30512
[12] Toshniwal R, Iqbal MZ, Ambulgekar R, Ghag NS, Bendale D, Chaware S. Hematoma Block as an Alternate Mode of Anesthesia for Management of Extra-Articular Distal End Radius Fracture with Percutaneous K-Wire Fixation in Emergency Department. J Orthop Case Rep. 2024;14(11):257-262. doi:10.13107/jocr.2024.v14.i11.4986
[13] Du Plessis P, Fournier MC. Management of complex wrist fractures with volar and dorsal locked (double-locked) K-lock. OTA Int. 2023;6(4):e286. Published 2023 Sep 22. doi:10.1097/OI9.0000000000000286
[14] Brennan SA, Kiernan C, Beecher S, et al. Volar plate versus k-wire fixation of distal radius fractures. Injury. 2016;47(2):372-376. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2015.08.040
[15] Sadat-Ali M, Shehri AM, AlHassan MA, et al. Broken Kirschner Wires Can Migrate: A Case Report and Review of Literature. J Orthop Case Rep. 2020;10(9):11-14. doi:10.13107/jocr.2020.v10.i09.1884
[16] Giordano V, Pires RES, Pesántez R, Kojima K, Koch HA. Expanding the Indications for Mini Plates in the Orthopedic Trauma Scenario: A Useful Alternative Technique for Maintaining Provisional Reduction and Improving Stability for Complex Periarticular Fracture Fixation of the Upper Limbs. J Orthop Case Rep. 2018;8(3):42-46. doi:10.13107/jocr.2250-0685.1100
[17] Dondapati A, Balamurugan P, Pandian H, Pradeep E, Kumar EVA, Mohideen S. Functional Outcome of Distal Radius Fractures Managed by Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis: A Prospective Study of 20 Patients. Journal of Orthopaedic Case Reports 2025 May, 15(05): 269-273
[18] Zong SL, Kan SL, Su LX, Wang B. Meta-analysis for dorsally displaced distal radius fracture fixation: volar locking plate versus percutaneous Kirschner wires. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10:108. Published 2015 Jul 15. doi:10.1186/s13018-015-0252-2
[19] Luttwak R, Ibelli TJ, Taub PJ, Melamed E, Wiser I. Predicting early term complications of ORIF distal radius fracture in outpatient settings using NSQIP data. Injury. Published online April 13, 2023. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2023.04.008
[20] Sahin MS, Gokkus K, Sargin MB. Ulnar Nerve and Ulnar Artery Injury Caused by Comminuted Distal Radius Fracture. J Orthop Case Rep. 2020;10(4):25-30. doi:10.13107/jocr.2020.v10.i04.1786
[21] Gökkus K, Sagtas E, Kesgin E, Aydin AT. Comminuted Distal Radial Fracture with Large Rotated Palmar Medial Osteochondral Fragment in the Joint. J Orthop Case Rep. 2018;8(1):27-31. doi:10.13107/jocr.2250-0685.984
[22] Tsuchiya F, Naito K, Mogami A, Obayashi O. New Technique for Dorsal Fragment Reduction in Distal Radius Fractures by Using Volar Bone Fenestration. J Orthop Case Rep. 2013;3(2):8-11. doi:10.13107/jocr.2250-0685.093