Comparison of Transverse and Vertical Incision Techniques in Ventral Approach for Bilateral Ovariectomy in Rats
Authors
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.main##
Abstract
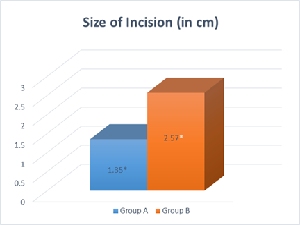
Objective: Ventral and dorsal surgical approaches are widely used for bilateral ovariectomy in animal experiments. The outcome of the surgery depends largely on the approach and incision used for conducting surgery. The present study compared the transverse and vertical incisions in the ventral approach with regard to the duration of the procedure, accessibility for the surgeon, number of sutures required, and time taken for wound healing and post-surgical mortality in rats. Design: A prospective study, conducted on 30 female wistar rats, at SGRRIM & HS, Dehradun for 6 months after approval from Institutional Animal Ethics Committee. Rats were randomly divided into 2 groups of 15 rats each. In Group A, rats underwent bilateral ovariectomy using transverse incision in ventral approach and in Group B, using vertical incision in ventral approach. Ketamine (80 mg/kg) and xylazine (10 mg/kg) were used intraperitoneally for anaesthesia. Comparison of surgical and post-surgical outcomes was done using Student T-test and Mann-Whitney U Test. The p-value < 0.05 was statistically significant. Results: The duration of surgical procedure in Group A was 15 ± 2.48 minutes and Group B was 29.47 ± 3.54 (p-value- 0.001), size of the incision in Group A was 1.35 ± 0.22 cm and Group B was 2.57 ± 0.40 (p-value- 0.001), number of sutures in Group A were 3.73 ± 0.80 and in Group B were 4.87 ± 0.92 (p-value- 0.003) and wound healing time in Group A was 2.87 ± 0.83 days and in Group B was 5.40 ± 0.83 days (p-value- 0.001). Conclusion: Study indicated that surgical and post-surgical outcomes by transverse incision for bilateral ovariectomy were significantly better than those by vertical incision. Further studies using a larger number of animals are needed to determine better incision in ventral approach.
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.details##
Copyright (c) 2025 Dr M. A Beg, Dr Shruti Malhotra, Dr Shalu Bawa, Dr Suman Bala, Dr Sangeeta Huidrom

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Creative Commons License All articles published in Annals of Medicine and Medical Sciences are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Dr Shruti Malhotra, Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmacology, SGRRIM & HS, Dehradun-248001, India.
*Corresponding author: Dr Shruti Malhotra; Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmacology, SGRRIM & HS, Dehradun-248001, India.
[1] Turner RT, Maran A, Lotinun S, Hefferan T, Evans GL, Zhang M, Sibonga JD. Animal models for osteoporosis. Rev. Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders. 2001 Jan;2(1):117-27.
[2] Giardino R, Fini M, Giaversi G, Mongiorgi R, Gnudi S, Zati A. Experimental surgical model in osteoporosis study. Bollettino della Societa Italiana di Biologia Sperimentale, 1993; 69 (7-8): 453-460.
[3] Sankar P, Veena P, Kumar R V S, Lakshmi N D, Kokila S. Ovariectomy in forty rats (Rattus norvegicus). Indian J. Anim. Res., 2014; 48 (5): 516-517. doi:10.5958/0976-0555.2014.00023.5
[4] Lasota A, Danowska-Klonowska D. Experimental osteoporosis- different methods of ovariectomy in female white rats. Annales Academiae Medicae Bialostocensis; 2004; 49(1):129-131.
[5] Khajuria DK, Razdan R, Mahapatra D. Description of a new method of ovariectomy in female rats. Revista brasileira de reumatologia. 2012 May-Jun; 52(3):462-70.
[6] Park SB, Lee YJ, Chung CK. Bone mineral density changes after ovariectomy in rats as an osteopenic model: stepwise description of double dorso-lateral approach. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2010 Oct; 48(4):309–312.
[7] Shirke SS, Jadhav SR, Jagtap AG. Methanolic extract of Cuminum cyminum inhibits ovariectomy-induced bone loss in rats. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2008 Nov; 233(11):1403–10.
[8] Sophocleous A, Idris AI. Rodent models of osteoporosis. Bonekey Rep. 2014 Dec 10; 3: 614. doi:10.1038/bonekey.2014.109
[9] Olson ME, Bruce J. Ovariectomy, Ovariohysterectomy and Orchidectomy in Rodents and Rabbits. Can Vet J. 1986 Dec; 27(12):523–527.
[10] Grantcharov TP, Rosenberg J. Vertical compared with transverse incisions in abdominal surgery. Eur J Surg. 2001 Apr; 167(4):260–267.
[11] Parhizkar S, Ibrahim R, Abdul Latiff L. Incision Choice in Laparatomy: A Comparison of Two Incision Techniques in Ovariectomy of Rats. World Appl Sci J. 2008 Jan; 4(4): 537-540.
[12] Brouwer EA, Dailey R, Brouwer JB. Ovariectomy of newborn rats: a descriptive surgical procedure. Lab Anim Sci. 1980 Jun; 30(3):546–548.
[13] Yousefzadeh N, Kashfi K, Jeddi S, Ghasemi A. Ovariectomized rat model of osteoporosis: a practical guide. EXCLI J. 2020 Jan 10; 19:89–107.
[14] Rigalli A, Di Loreto V. Experimental surgical models in the laboratory rat. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 2016.
[15] Popović T, Šrbić R, Matavulj M, Obradović Z, Sibinčić S. Experimental model of osteoporosis on 14 weeks old ovariectomised rats: biochemical, histological and biomechanical study. Biol Serbica. 2016; 38(1): 18-27.