Evaluating Management Strategies for Appendicular Mass: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Conservative Versus Surgical Approaches
Authors
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.main##
Abstract
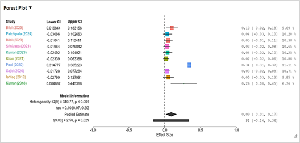
Background: Acute appendicitis is a frequent emergent situation that necessitates surgery. Complications, including an appendiceal mass, occur in 2-10% of appendicitis cases. Management of appendicular mass remains controversial, from non-operative to operative. Aim and Objective: This meta-analysis and systematic review were intended to determine how well conservative management could match up against early appendicular mass. One of the questions underlying this research was: “Can conservative management offer the same results as surgery with fewer complications and hospitalization?”. Methods: Electronic databases such as PubMed, Embase, and Scopus were searched from 2015-2024 and 1378 studies were retrieved. Thirteen studies were finally included. Results: The overall success rate with conservative management was 90% (95% CI: 87-94) and complications were at a rate of 10% (95% CI: 8-11). However, the complication rate with the surgical approach was 19% (95% CI: 15-22). The recurrence rates for conservative management were 9% (95% CI: 1-17). Conclusion: Conservative treatment of appendicular mass is effective and less complex than early appendectomy indicating that it may be a viable first line of treatment. Standard treatment protocols will need to be established through further high-quality studies.
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.details##
Copyright (c) 2025 Satheesh Kumar M, Abdul Saleem M, Shahul Hameed, Jamila Hameed

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Creative Commons License All articles published in Annals of Medicine and Medical Sciences are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
[1] Hoffmann J, Lindhard A, Jensen HE. Appendix mass: conservative management without interval appendectomy. The American journal of surgery. 1984 Sep 1;148(3):379-82.
[2] Willemsen PJ, Hoorntje LE, Eddes EH, Ploeg RJ. The need for interval appendectomy after resolution of an appendiceal mass questioned. Digestive surgery. 2002 Jul 4;19(3):216-22.
[3] Moher D, Stewart L, Shekelle P. Implementing PRISMA-P: recommendations for prospective authors. Systematic reviews. 2016 Dec; 5:1-2.
[4] Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, Tugwell P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses.
[5] Demetrashvili Z, Kenchadze G, Pipia I, Ekaladze E, Kamkamidze G. Management of appendiceal mass and abscess. An 11-year experience. International Surgery. 2015 Jun 1;100(6):1021-5.
[6] Yang Z, Sun F, Ai S, Wang J, Guan W, Liu S. Meta-analysis of studies comparing conservative treatment with antibiotics and appendectomy for acute appendicitis in the adult. BMC surgery. 2019 Dec;19:1-0.
[7] Forsyth J, Lasithiotakis K, Peter M. The evolving management of the appendix mass in the era of laparoscopy and interventional radiology. The Surgeon. 2017 Apr 1;15(2):109-15.
[8] Lasson Å, Lundagårds J, Lorén I, Nilsson PE. Appendiceal abscesses: primary percutaneous drainage and selective interval appendicectomy. European Journal of Surgery. 2002 Aug;168(5):264-9.
[9] Ram KR, Chandana S, Koshti S. A study of outcome of non-operative versus operative management in 50 cases of appendicular lump. Int Surg J. 2017 Jul;4:2233-7.
[10] Kumar R, Madeshiya S, Pandey VK, Shankhdhar A. Comparative analysis of early exploration versus conservative approach for management of appendiceal mass. Int Surg J. 2018 Dec;5(12):3868.
[11] Gilkar IA, Mushtaq U, Peer JA, Mir BA, Hassan Y, Dar WA. Management of appendicular lump at tertiary care hospital. Group (a). 2019;46(26):1-76.
[12] Lotfallah A, Aamery A, Moussa G, Manu M. Surgical versus conservative management of acute appendicitis during the COVID-19 pandemic: a single-centre retrospective study. Cureus. 2021 Mar 24;13(3).
[13] Sajid MS, Ray K, Hebbar M, Riaz W, Baig MK, Sains P, Singh KK. South Coast appendicular mass management (SCAM) survey. Translational Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2020 Jan 5;5:4.
[14] de Almeida Leite RM, Seo DJ, Gomez-Eslava B, Hossain S, Lesegretain A, de Souza AV, Bay CP, Zilberstein B, Marchi E, Machado RB, Barchi LC. Nonoperative vs operative management of uncomplicated acute appendicitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA surgery. 2022 Sep 1;157(9):828-34.
[15] van Amstel P, Sluckin TC, van Amstel T, van der Lee JH, de Vries R, Derikx JP, Bakx R, van Heurn LE, Gorter RR. Management of appendiceal mass and abscess in children; early appendectomy or initial non-operative treatment? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Surgical endoscopy. 2020 Dec;34:5234-49.
[16] Khan FA, Paudel N, Maharjan P. Comparative study between conservative management and appendectomy in appendicular lump in children. Journal of Nepalgunj Medical College. 2021 Dec 31;19(2):23-6.
[17] Napar NB, Shaikh NA, Baloch I, Shah AA, Shaikh B, Mahtam I. Early surgery for appendicular lump in pediatric patients is still safe. The Professional Medical Journal. 2022 Feb 28;29(03):280-4.
[18] Israr S, Akhtar J, Taqvi SM, Zamir N. Early surgical management of appendicular mass in pediatric patients. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2021 Mar 1;31(3):302-6.
[19] Rajah KH, Menon S, Ramachandran G. Current management of appendicular mas-a narrative. Med J Malaysia. 2023 Sep;78(5):669.
[20] Appa SK, Kumar KK, Vuppala C. Appendicular Mass: Early OrInterval Appendicectomy. Int J Acad Med Pharm. 2023;5(1):787-93.
[21] Tarar B, Batool S, Majeed S, Saleem A, TARAR BA. Comparison between early appendectomy vs. conservative management in cases of appendicular mass. Cureus. 2023 Apr 22;15(4).
[22] Bancke Laverde BL, Maak M, Langheinrich M, Kersting S, Denz A, Krautz C, Weber GF, Grützmann R, Brunner M. Risk factors for postoperative morbidity, prolonged length of stay and hospital readmission after appendectomy for acute appendicitis. European Journal of Trauma and Emergency Surgery. 2023 Jun;49(3):1355-66.
[23] Nandan PP, Prakash GV, Reddy VM, Harish NV, Nagamaninikhila A. A Clinical Study on Appendicular Mass and ITS Outcome. Surg. J. 2024 Sep 14;19:6-19.