Effectiveness of Teaching with Riddles Using Team-Based Learning: A Prospective Study on Third Phase (1) Medical Students
Authors
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.main##
Abstract
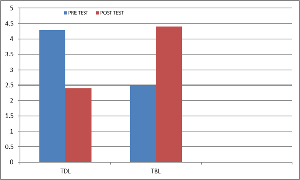
Background and Objectives: The study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of teaching toxicology using "Toxic Riddles" in a Team-Based Learning (TBL) format compared to traditional didactic lectures (TDL). The objectives were to assess the impact of this novel teaching approach on student learning outcomes and to explore student perceptions and attitudes toward TBL in the context of clinical toxicology education. Materials and Methods: This prospective study was conducted on third-year medical undergraduates at a tertiary medical institution. Ethics approval was obtained from the institutional ethics committee. A controlled comparison between TBL and TDL was performed using a modified crossover design. Two critical topics from chemical toxicology, Pesticides Poisoning (PP) and Corrosives Poisoning (CP), were selected for the TBL sessions. These topics were chosen due to their high incidence in our hospital. TBL sessions were structured around clinical scenarios where students worked in teams to analyze cases, make evaluative decisions, and formulate management plans for poisoned patients. The effectiveness of TBL was assessed through pre- and post-intervention tests, while student perceptions were gathered using structured questionnaires. Results: The results indicated that students in the TBL group showed a statistically significant improvement in their post-test scores compared to the TDL group (10.61% vs 4.23%, mean difference 6.38%, 95% CI 0.7-8.3%, p = 0.021). Conclusion: The use of toxic riddles in a TBL format proved to be an effective and engaging method for teaching clinical toxicology, outperforming traditional didactic lectures in both student learning outcomes and satisfaction.
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.details##
Copyright (c) 2025 Richa Choudhary, Pradeep Kumar Yadav, Krishna Kumar Singh, Madhulika Shukla, Vivek Pathak, Satendra Mohan, Dileep Kumar Yadav

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Creative Commons License All articles published in Annals of Medicine and Medical Sciences are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
[1] Parmelee D, Michaelsen LK, Cook S, Hudes PD. Team-based learning: a practical guide: AMEE guide no 65. Med Teach. 2012;34: e275–87.
[2] Burgess, A., van Diggele, C., Roberts, C. et al. Team-based learning: design, facilitation and participation. BMC Med Educ 20 (Suppl 2), 461 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-020-02287-y
[3] Cevik AA, ElZubeir M, Abu-Zidan FM, Shaban S. Team-based learning improves knowledge and retention in an emergency medicine clerkship. Int J Emerg Med. (2019) 12:6. [https://doi.org/10.1186/s12245-019-0222-2]
[4] Faezi ST, Moradi K, GhafarRahimi Amin A, Akhlaghi M, Keshmiri F. The effects of team-based learning on learning outcomes in a course of rheumatology. J Adv Med Educ Prof. 2018 Jan;6(1):22-30. PMID: 29344526; PMCID: PMC5757153.
[5] Alizadeh, M., Masoomi, R., Mafinejad, M.K. et al. Team-based learning in health professions education: an umbrella review. BMC Med Educ 24, 1131 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-06147-x
[6] Iramaneerat C, Samranpanist O, Pasarat S, Anatakanchai M. Assessing the outcomes of team-based learning in surgery. J Med Assoc Thai. (2017) 100:24. [Available online at: http://www.jmatonline.com/index.php/jmat/article/view/ 8159]
[7] Boysen-Osborn M et al.TheToxiscapeHunt:An Escape room Scavenger hunt for Toxicology education.JETem 2018.3(1):SG9-19. [https://doi.org/10.21980/J8NW5B]
[8] Cevik AA, ElZubeir M, Abu-Zidan FM, Shaban S. Team-based learning improves knowledge and retention in an emergency medicine clerkship. Int J Emerg Med. (2019) 12:6. [https://doi.org/10.1186/s12245-019-0222-2]
[9] Darlow B, Coleman K, McKinlay E, et al. The positive impact of interprofessional education: A controlled trial to evaluate a programme for health professional students. BMC Med Educ. 2015; 15:98. [https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-015-0385-3]
[10] Michaelsen LK, Knight AB, Fink LD, editors. Team-based learning: A transformative use of small groups in college teaching. Taylor & Francis; 2023 Jul 3. [Available at https://books.google.co.in/books?hl=en&lr=&id=_A7JEAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PT6&dq=9.%09Michaelsen+LK,+Knight+AB,+Fink+LD,+editors.+Team-based+Learning:+A+Transformative+Use+of+Small+Groups.+Westport,+CT:+Praeger%3B+2002.+%5BGoogle+Scholar%5D&ots=frpSaD345P&sig=DE-yc2iXytH7jUzJkZRny6k38XI&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false]
[11] Clark Michele C, Nguyen Hoang T, Bray C, Levine Ruth E. Team-based learning in an undergraduate nursing course. J Nurs Educ. (2008) 47:111–7. [https://doi.org/10.3928/01484834-20080301-02]
[12] Blouin RA, Riffee WH, Robinson ET, Beck DE, Green C, Joyner PU, Persky AM, Pollack GM. Roles of innovation in education delivery. Am J Pharm Educ. 2009 Dec 17;73(8):154. doi: 10.5688/aj7308154. PMID: 20221347; PMCID: PMC2828315.
[13] Parmelee D, Michaelsen LK, Cook S, Hudes PD. Team-based learning: a practical guide: AMEE guide no. 65. Med Teach. 2012;34(5):e275–e287. [https://doi.org/10.3109/0142159X.2012.651179]