Advancements in AI for Obesity Prediction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Authors
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.main##
Abstract
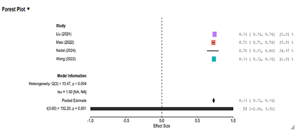
Background: The worldwide prevalence of obesity has reached an epidemic level and has presented a significant burden to public health infrastructure. There is a critical need for novel predictive instruments, and computerized intelligent systems (artificial intelligence or AI), specifically machine learning (ML), are an appealing method to precisely forecast obesity and associated health outcomes. Nonetheless, an extensive summary of recent evidence on the efficacy and usage of these models remains a critical void within literature. Aim and Objective: The principal research question to be addressed is: “What is the overall predictive efficacy of computer and machine-based intelligence systems in the prediction of obesity and overweight status in adult and adolescent populations?” Methods: Systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted on articles released in the time period 2020 to 2025. The databases used in this review were PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Embase. The relevant literature was searched by using the application of keywords and Boolean operators, namely "obesity," "overweight," "artificial intelligence," "machine learning," "deep learning," and "prediction." The total of ten studies were covered in the systematic review while four studies were chosen to be used in the meta-analysis. The quality of the studies were assessed by using Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS). A meta-analysis was undertaken using a random-effects model to calculate the pooled effect size, standard error, and 95% confidence interval with statistical analysis being done in RStudio. Results: A total of 307 studies were identified by the database searching. 92 duplicates and 215 abstracts were removed by screening. The full systematic review covered 10 studies. The meta-analysis in four of these studies with a pooled sample size of 363,731 produced a pooled effect size (proportion) of 0.730 (95% CI = 0.719 to 0.741) demonstrating a strong degree of predictive accuracy. Conclusion: Artificial intelligence and machine learning models consistently exhibit superior predictive capabilities in estimating obesity and overweight conditions. The results underscore the clinical significance of these models as essential instruments for early prevention and intervention efforts, providing an accurate methodology to tackle the public health challenge posed by obesity.
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.details##
Copyright (c) 2025 Veerakesari S, Sarathlal S, Aleena Thomas Cheeran, Noula Rahim, Jamila Hameed

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Creative Commons License All articles published in Annals of Medicine and Medical Sciences are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Veerakesari S, Department of General Medicine, Karuna Medical College, Vilayodi, Chittur, Palakkad, Kerala, India.
Department of General Medicine, Karuna Medical College, Vilayodi, Chittur, Palakkad, Kerala, India.
Sarathlal S, Department of General Medicine, Karuna Medical College, Vilayodi, Chittur, Palakkad, Kerala, India.
Department of General Medicine, Karuna Medical College, Vilayodi, Chittur, Palakkad, Kerala, India.
Aleena Thomas Cheeran, Department of General Medicine, Karuna Medical College, Vilayodi, Chittur, Palakkad, Kerala, India.
Department of General Medicine, Karuna Medical College, Vilayodi, Chittur, Palakkad, Kerala, India.
Noula Rahim, Department of Biochemistry, Karuna Medical College, Vilayodi, Chittur, Palakkad, Kerala, India.
Department of Biochemistry, Karuna Medical College, Vilayodi, Chittur, Palakkad, Kerala, India.
Jamila Hameed, Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Karuna Medical College, Vilayodi, Chittur, Palakkad, Kerala, India.
Research Mentor, Emiratus Professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Karuna Medical College, Vilayodi, Chittur, Palakkad, Kerala, India.
[1] Azmi S, Kunnathodi F, Alotaibi HF, Alhazzani W, Mustafa M, Ahmad I, Anvarbatcha R, Lytras MD, Arafat AA. Harnessing Artificial Intelligence in Obesity Research and Management: A Comprehensive Review. Diagnostics. 2025 Feb 6;15(3):396.
[2] Gasmi A. Machine learning and bioinformatics for diagnosis analysis of obesity spectrum disorders. arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.03139. 2022 Aug 5.
[3] Bhatia A, Smetana S, Heinz V, Hertzberg J. Modeling obesity in complex food systems: Systematic review. Frontiers in Endocrinology. 2022 Oct 13;13:1027147.
[4] Tsolakidis D, Gymnopoulos LP, Dimitropoulos K. Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies for personalized nutrition: a review. InInformatics 2024 Aug 28 (Vol. 11, No. 3, p. 62). MDPI.
[5] Kassem H, Beevi AA, Basheer S, Lutfi G, Cheikh Ismail L, Papandreou D. Investigation and assessment of AI’s role in nutrition—an updated narrative review of the evidence. Nutrients. 2025 Jan 5;17(1):190.
[6] Masi D, Risi R, Biagi F, Vasquez Barahona D, Watanabe M, Zilich R, Gabrielli G, Santin P, Mariani S, Lubrano C, Gnessi L. Application of a machine learning technology in the definition of metabolically healthy and unhealthy status: a retrospective study of 2567 subjects suffering from obesity with or without metabolic syndrome. Nutrients. 2022 Jan 15;14(2):373.
[7] Jaksic M, Martinovic M, Gligorovic-Barhanovic N, Antunovic T, Nedovic-Vukovic M. Relationship between insulin-like growth factor-1, insulin resistance and metabolic profile with pre-obesity and obesity in children. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Feb 23;34(3):301-309.
[8] Szydlowska-Gladysz J, Gorecka AE, Stepien J, Rysz I, Ben-Skowronek I. IGF-1 and IGF-2 as molecules linked to causes and consequences of obesity from fetal life to adulthood: a systematic review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024 Apr 2;25(7):3966.
[9] Haldrup D, Wei C, Holland-Fischer P, Kristensen K, Rittig S, Lange A, Hørlyck A, Solvig J, Grønbæk H, Birkebæk NH, Frystyk J. Effects of lifestyle intervention on IGF-1, IGFBP-3, and insulin resistance in children with obesity with or without metabolic-associated fatty liver disease. Eur J Pediatr. 2023 Feb;182(2):855-865.
[10] Chang HR, Kim HJ, Xu X, Ferrante AW Jr. Macrophage and adipocyte IGF1 maintain adipose tissue homeostasis during metabolic stresses. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2016 Jan;24(1):172-83.
[11] Wong JE, Yamaguchi M, Nishi N, Araki M, Wee LH. Predicting overweight and obesity status among Malaysian working adults with machine learning or logistic regression: retrospective comparison study. JMIR formative research. 2022 Dec 7;6(12):e40404.
[12] Sidik SM, Rampal L. The prevalence and factors associated with obesity among adult women in Selangor, Malaysia. Asia Pacific family medicine. 2009 Apr 9;8(1):2.
[13] Chong CT, Lai WK, Mohd Sallehuddin S, Ganapathy SS. Prevalence of overweight and its associated factors among Malaysian adults: Findings from a nationally representative survey. PLoS One. 2023 Aug 2;18(8):e0283270.
[14] Tan AK, Yen ST, Feisul MI. Determinants of body weight status in Malaysia: an ethnic comparison. Int J Public Health. 2012 Apr;57(2):279-88. doi: 10.1007/s00038-011-0238-8.
[15] An R, Shen J, Xiao Y. Applications of Artificial Intelligence to Obesity Research: Scoping Review of Methodologies. J Med Internet Res. 2022 Dec 7;24(12):e40589.
[16] Sewpaul R, Awe OO, Dogbey DM, Sekgala MD, Dukhi N. Classification of Obesity among South African Female Adolescents: Comparative Analysis of Logistic Regression and Random Forest Algorithms. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;21(1):2. Published 2023 Dec 19.
[17] Ferreras A, Sumalla-Cano S, Martínez-Licort R, Elío I, Tutusaus K, Prola T, Vidal-Mazón JL, Sahelices B, de la Torre Díez I. Systematic Review of Machine Learning applied to the Prediction of Obesity and Overweight. J Med Syst. 2023 Jan 13;47(1):8.
[18] Zulfarina MS, Sharif R, Mokhtar SA, Shuid AN, Naina-Mohamed I. Lifestyle indices of body composition and obesity risk and prevalence among multi-ethnic adolescents in Malaysia. Front Pediatr. 2022;10:899014. Published 2022 Nov 1.
[19] Choong C, Brnabic A, Chinthammit C, Ravuri M, Terrell K, Kan H. Applying machine learning approaches for predicting obesity risk using US health administrative claims database. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2024 Sep 26;12(5):e004193.
[20] Delpino FM, Costa ÂK, do Nascimento MC, Moura HS, Dos Santos HG, Wichmann RM, Chiavegatto Filho AD, Arcêncio RA, Nunes BP. Does machine learning have a high performance to predict obesity among adults and older adults? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases. 2024 Sep 1;34(9):2034-45.
[21] Liu H, Wu YC, Chau PH, Chung TW, Fong DY. Prediction of adolescent weight status by machine learning: a population-based study. BMC Public Health. 2024 May 20;24(1):1351.
[22] Nadal E, Benito E, Ródenas-Navarro AM, Palanca A, Martinez-Hervas S, Civera M, Ortega J, Alabadi B, Piqueras L, Ródenas JJ, Real JT. Machine learning model in obesity to predict weight loss one year after bariatric surgery: A pilot study. Biomedicines. 2024 May 25;12(6):1175.
[23] Saux P, Bauvin P, Raverdy V, Teigny J, Verkindt H, Soumphonphakdy T, Debert M, Jacobs A, Jacobs D, Monpellier V, Lee PC. Development and validation of an interpretable machine learning-based calculator for predicting 5-year weight trajectories after bariatric surgery: a multinational retrospective cohort SOPHIA study. The Lancet Digital Health. 2023 Oct 1;5(10):e692-702.
[24] Veneziani I, Grimaldi A, Marra A, Morini E, Culicetto L, Marino S, Quartarone A, Maresca G. Towards a Deeper Understanding: Utilizing Machine Learning to Investigate the Association between Obesity and Cognitive DeclineA Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024 Apr 16;13(8):2307.