Impact of Renal Function on Apixaban and Rivaroxaban Use in Stroke Patients with Atrial Fibrillation
Authors
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.main##
Abstract
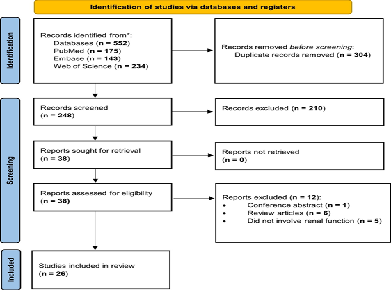
Objective: To assess how renal function influences the efficacy and safety of Apixaban and Rivaroxaban in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Design: Systematic review following PRISMA guidelines. Methods: A comprehensive literature search identified studies published between 2018 and 2024 evaluating Apixaban or Rivaroxaban use in AF patients with varying degrees of renal impairment. Twenty-six studies meeting the inclusion criteria were reviewed for outcomes related to stroke prevention, bleeding risk, and dose adjustment. Results: Apixaban and Rivaroxaban were both effective in stroke prevention among AF patients with CKD. However, Apixaban consistently demonstrated a superior safety profile, with lower rates of major bleeding, particularly in patients with moderate to severe CKD or on dialysis. This benefit is attributed to Apixaban’s lower renal clearance compared with Rivaroxaban, which often requires dose modification in renal impairment. Most studies favored Apixaban for patients with advanced CKD, while Rivaroxaban use was associated with higher bleeding risk in severe renal dysfunction. Conclusion: Apixaban offers favorable safety and comparable efficacy to Rivaroxaban in AF patients with CKD. Individualized anticoagulation strategies guided by renal function are essential, and further studies are warranted in end-stage renal disease populations.
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.details##
Copyright (c) 2025 Wilhelmina N. Hauwanga, Abisola M. Olowofeso, Amoolya R. Amaravadhi, Marwa A. Kdouk, Johny Davilma, Onyinye E. Ebiliekwe, Ifunanya R. Ekeocha, Abdelwahab Ahmed, Pranav Tiyyala, Hassan A. Ahmed, Billy McBenedict

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Creative Commons License All articles published in Annals of Medicine and Medical Sciences are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Wilhelmina N. Hauwanga, Cardiology, Faculty of Medicine, Federal University of the State of Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
Cardiology, Faculty of Medicine, Federal University of the State of Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
Abisola M. Olowofeso, Public Health, University of Illinois, Springfield, USA.
Public Health, University of Illinois, Springfield, USA.
Amoolya R. Amaravadhi, Internal Medicine, Malla Reddy Institute of Medical Sciences, Hyderabad, India.
Internal Medicine, Malla Reddy Institute of Medical Sciences, Hyderabad, India.
Marwa A. Kdouk, Medicine, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China.
Medicine, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China.
Johny Davilma, Internal Medicine, St Elizabeth Youngstown Hospital - Neomed, Youngstown, USA.
Internal Medicine, St Elizabeth Youngstown Hospital - Neomed, Youngstown, USA.
Onyinye E. Ebiliekwe, Internal Medicine, Nnamdi Azikiwe University Teaching Hospital, Nnewi, Nigeria.
Internal Medicine, Nnamdi Azikiwe University Teaching Hospital, Nnewi, Nigeria.
Ifunanya R. Ekeocha, Internal Medicine, Nnamdi Azikiwe University Teaching Hospital, Nnewi, Nigeria.
Internal Medicine, Nnamdi Azikiwe University Teaching Hospital, Nnewi, Nigeria.
Abdelwahab Ahmed, Neurosurgery, Fluminense Federal University, Niterói, Brazil.
Neurosurgery, Fluminense Federal University, Niterói, Brazil.
Pranav Tiyyala, Neurosurgery, Fluminense Federal University, Niterói, Brazil.
Neurosurgery, Fluminense Federal University, Niterói, Brazil.
Hassan A. Ahmed, Internal Medicine, Kassala University Hospital, Kassala, Sudan
Internal Medicine, Kassala University Hospital, Kassala, Sudan
[1] Sagris M, Vardas EP, Theofilis P, Antonopoulos AS, Oikonomou E, Tousoulis D: Atrial Fibrillation: Pathogenesis, Predisposing Factors, and Genetics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022, 23:6. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010006
[2] Moras E, Gandhi K, Yakkali S, Frishman WH, Aronow WS: Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion as a Strategy for Reducing Stroke Risk in Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation. Cardiology in Review. 2024, 10.1097/CRD.0000000000000757. https://doi.org/10.1097/CRD.0000000000000757
[3] Wang X, Ouyang M, Yang J, Song L, Yang M, Anderson CS: Anticoagulants for acute ischaemic stroke. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2021, 2021:. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd000024.pub5
[4] Alberts MJ, Eikelboom JW, Hankey GJ: Antithrombotic therapy for stroke prevention in non-valvular atrial fibrillation. The Lancet Neurology. 2012, 11:1066–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70258-2
[5] Kim S, Jeong Y, Kim YL, et al.: Association of Chronic Kidney Disease with Atrial Fibrillation in the General Adult Population: A Nationwide Population‐Based Study. JAHA. 2023, 12:e028496. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.122.028496
[6] Potpara TS, Lenarczyk R, Larsen TB, Deharo J-C, Chen J, Dagres N, Conducted by the Scientific Initiatives Committee EHRA: Management of atrial fibrillation in patients with chronic kidney disease in Europe Results of the European Heart Rhythm Association Survey. EP Europace. 2015, 17:1862–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/euv416
[7] Coleman CI, Kreutz R, Sood NA, Bunz TJ, Eriksson D, Meinecke A-K, Baker WL: Rivaroxaban Versus Warfarin in Patients With Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation and Severe Kidney Disease or Undergoing Hemodialysis. The American Journal of Medicine. 2019, 132:1078–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2019.04.013
[8] Jansson M, Själander S, Sjögren V, Björck F, Renlund H, Norrving B, Själander A: Reduced dose direct oral anticoagulants compared with warfarin with high time in therapeutic range in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2023, 55:415–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-022-02763-w
[9] Esteve Pastor M, Marin F, Anguita M, et al.: 2MACE score predicts cardiovascular adverse events in real-world atrial fibrillation patients under rivaroxaban therapy. Data from EMIR study. European Heart Journal. 2021, 42:ehab724.2484. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehab724.2484
[10] Page MJ, Moher D, Bossuyt PM, et al.: PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021, n160. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n160
[11] Albabtain MA, Alanazi ZD, Al-Mutairi NH, Alyafi O, Albanyan R, Arafat AA: Real-world Experience in Managing Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Renal Impairment; Rivaroxaban versus Warfarin. Heart Views. 2023, 24:136–40. https://doi.org/10.4103/heartviews.heartviews_117_22
[12] Burgos KD, Sienko SE, Hoffman JL, Koerber JM, Smythe MA: Characteristics, Management, and Outcomes of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Experiencing a Major Bleeding Event While on Rivaroxaban. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2018, 24:372–8. https://doi.org/10.1177/1076029616684030
[13] Carnicelli AP, Hong H, Connolly SJ, et al.: Direct Oral Anticoagulants Versus Warfarin in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: Patient-Level Network Meta-Analyses of Randomized Clinical Trials with Interaction Testing by Age and Sex. Circulation. 2022, 145:242–55. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.056355
[14] Cerdá M, Cerezo-Manchado JJ, Johansson E, et al.: Facing real-life with direct oral anticoagulants in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: outcomes from the first observational and prospective study in a Spanish population. Journal of Comparative Effectiveness Research. 2018, 8:165–78. https://doi.org/10.2217/cer-2018-0134
[15] Cho MS, Yun JE, Park JJ, et al.: Outcomes After Use of Standard- and Low-Dose Non–Vitamin K Oral Anticoagulants in Asian Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Stroke. 2019, 50:110–8. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.023093
[16] De Vriese AS, Caluwé R, Van Der Meersch H, De Boeck K, De Bacquer D: Safety and Efficacy of Vitamin K Antagonists versus Rivaroxaban in Hemodialysis Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. JASN. 2021, 32:1474–83. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2020111566
[17] Garlo K, Mavrakanas T, Wang W, Burdick E, Charytan D: Stroke and Major Bleeding when Switching from Warfarin to Apixaban in Patients with Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease and Prevalent Atrial Fibrillation. 2021. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-144190/v1
[18] Heleniak Z, Papuga-Szela E, Krzysztof P, Anetta U: Efficacy and Safety of Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Chronic Kidney Disease Stage G4: A Single-Center Experience. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology. 2020, 76:671–7. https://doi.org/10.1097/FJC.0000000000000911
[19] Ibáñez L, Sabaté M, Vidal X, et al.: Incidence of direct oral anticoagulant use in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation and characteristics of users in 6 European countries (2008–2015): A cross‐national drug utilization study. Brit J Clinical Pharma. 2019, 85:2524–39. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.14071
[20] Jackevicius CA, Lu L, Ghaznavi Z, Warner AL: Bleeding Risk of Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation. Circ: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes. 2021, 14:e007230. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.120.007230
[21] Jones MJ, Eudaley ST, Moye RA, Hodge TA, Nesbit RM, Franks AS: Safety outcomes of apixaban in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation and severe renal impairment. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2020, 50:330–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-019-02028-z
[22] Kreutz R, Deray G, Floege J, et al.: Risk Profiles and Treatment Patterns in Atrial Fibrillation Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Receiving or not Receiving Anticoagulation Therapy. TH Open. 2024, 08:e106–13. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0044-1780529
[23] Kreutz R, Deray G, Floege J, et al.: Rivaroxaban vs Vitamin K Antagonist in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease. JACC: Advances. 2024, 3:100813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacadv.2023.100813
[24] Lee S-R, Choi E-K, Han K-D, Jung J-H, Cha M-J, Oh S, Lip GYH: Non–Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants in Asian Patients with Supranormal Renal Function. Stroke. 2019, 50:1480–9. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.024264
[25] Minematsu K, Ikeda T, Ogawa S, et al.: Real-World Outcomes of Rivaroxaban Treatment in Patients with Both Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation and a History of Ischemic Stroke/Transient Ischemic Attack. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2019, 48:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1159/000502883
[26] Navarro-Almenzar B, Cerezo-Manchado JJ, García-Candel F: Real life behaviour of direct oral anticoagulants in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation and morbid obesity. IJC Heart & Vasculature. 2021, 37:100913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcha.2021.100913
[27] Ngufor C, Yao X, Inselman JW, et al.: Identifying treatment heterogeneity in atrial fibrillation using a novel causal machine learning method. American Heart Journal. 2023, 260:124–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ahj.2023.02.015
[28] Perez-Bernat E, Viñas Ma A, Vera M, et al.: Non-valvular atrial fibrillation in patients on peritoneal dialysis, prevalence, treatment and professionals involved. Nefrología (English Edition). 2024, 44:268–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nefroe.2024.03.008
[29] Perreault S, Boivin Proulx L-A, Lenglet A, Massy ZA, Dorais M: Effectiveness and safety of apixaban and rivaroxaban vs warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation and chronic kidney disease. World J Nephrol. 2023, 12:132–46. https://doi.org/10.5527/wjn.v12.i5.132
[30] Pinto SS, Teixeira A, Henriques TS, Monteiro H, Martins C: AF-React study: Prevalence of thrombotic events in patients with atrial fibrillation receiving NOACs – real-world data analysis from northern Portugal primary healthcare. Front Med. 2024, 11:1273304. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2024.1273304
[31] Pokorney SD, Black-Maier E, Hellkamp AS, et al.: Oral Anticoagulation and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and End-Stage Renal Disease. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2020, 75:1299–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2020.01.019
[32] Tittl L, Marten S, Naue C, Beyer-Westendorf J: Patterns of atrial fibrillation anticoagulation with rivaroxaban — 7-year follow-up from the Dresden NOAC registry. Thrombosis Research. 2024, 236:61–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2024.02.014
[33] Wetmore JB, Weinhandl ED, Yan H, Reyes JL, Herzog CA, Roetker NS: Apixaban Dosing Patterns Versus Warfarin in Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation Receiving Dialysis: A Retrospective Cohort Study. American Journal of Kidney Diseases. 2022, 80:569-579.e1. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2022.03.007
[34] Yun S, Sevinsky R, Spracklin T, Tatara A, Fenves AZ: Relation of apixaban bleeding rates to dose in patients with chronic kidney disease. Baylor University Medical Center Proceedings. 2021, 34:555–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/08998280.2021.1930967