Bridging the Gap: Attitudes Towards Communication Skills and Their Assessment in Medical Education
Authors
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.main##
Abstract
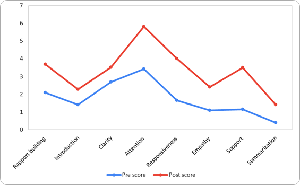
Objectives: 1. To assess MBBS Phase III-Part-1 medical student’s attitudes towards need of communication skills. 2. To assess communication skills among MBBS Phase III-Part-1 medical students. Methodology: This is an interventional study conducted among MBBS Phase 3 students of a medical college to assess students’ attitude towards need of communication skills in medical education and observed communication skill scale to assess communication skill before and after educational intervention. Data was analysed for descriptive statistics and paired t test for determining association. Results: Impact of educational intervention on communication skills and attitudes towards need of communication skills in medical education. Gender-based comparisons revealed no statistically significant differences. Observed communication skills assessment score also improved notably post-intervention. Rapport building increased from 2.10 to 3.69, attention and patience while listening rose from 3.42 to 5.81, and responsiveness improved from 1.65 to 4.00. Conclusion: There was a positive change in attitude towards need of communication skill. Significant improvement in skills was observed among both genders.
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.details##
Copyright (c) 2025 Dr Shwetha Hariba, Dr Divyarani MN, Dr Sowmya SM

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Creative Commons License All articles published in Annals of Medicine and Medical Sciences are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Dr Shwetha Hariba, Associate Professor, Department of Community Medicine, Shri Atal Bihari Vajpayee Medical college and RI, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India.
Associate Professor, Department of Community Medicine, Shri Atal Bihari Vajpayee Medical college and RI, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India.
Dr Divyarani MN, Associate Professor, Department of Pathology, Shri Atal Bihari Vajpayee Medical college and RI, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India.
Associate Professor, Department of Pathology, Shri Atal Bihari Vajpayee Medical college and RI, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India.
Dr Sowmya SM, Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology, Shri Atal Bihari Vajpayee Medical college and RI, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India.
Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology, Shri Atal Bihari Vajpayee Medical college and RI, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India.
[1] Dacre, Richardson, Noble et al. Communication skills training in postgraduate medicine: the development of a new course. Postgrad Med J 2004; 80:711–715.
[2] Joyce BL, Scher E, Steenbergh T, Voutt-Goos MJ. Development of an institutional resident curriculum in communication skills. J Grad Med Educ. 2011 December; 3(4): 524–528.
[3] Kellie Bennett and Zaza Lyons. Communication Skills in Medical Education: An Integrated Approach. Education Research and Perspectives.2011;38(2):45-56.)
[4] Nilesh Chavda, Priti Solanky, Jatin V Dhanani, Aashal Shah, Nirav Patel et. al. Assessment of Clinical Communication Skills of Medical Students Through the Simulated Patient Approach. JMedEdu.2020August;19(3): e108661.
[5] Ellemieke Rasenberg, Guus Brand, Evelyn van Weel-Baumgarten. Integrating medical and practical skills in communication skills training: Do students feel it supports them with transfer from classroom to practice?. PEC Innovation 2 (2023) 100158:1-7.
[6] National Medical Commission. AETCOM Book: Attitude, Ethics and Communication Module for Undergraduate Medical Education. 2020. https://www.nmc.org.in/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/AETCOM_book.pdf
[7] KNUT ASPEGREN BEME Guide No. 2: Teaching and learning communication skills in medicine-a review with quality grading of articles. Medical Teacher; Vol. 21(6) 1999:563-70.
[8] Manisha Nagpal, Sahiba Kukreja, Sarthak Chawla. Teaching and assessing communication skills as an element of early clinical exposure (ECE) in first year medical students. Indian Journal of Forensic and Community Medicine. 2023;10(1):33-37.
[9] Rees C, Sheard C. The development of a scale to measure medical students' attitudes towards learning communication skills: the Communication Skills Attitude Scale (CSAS). Med Educ. 2002;36(2):141-147.
[10] Chauhan A, et al. Observed Communication Skills Checklist: A tool for assessing clinical communication skills. J Med Edu. 2019;19(3):e108661.
[11] Dacre, Richardson, Noble et al. Communication skills training in postgraduate medicine: the development of a new course. Postgrad Med J 2004; 80:711-715.