Clinical Effectiveness and Safety of Cefixime in Managing Typhoid Fever in Indian Population: A Real-world Evidence Study
Authors
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.main##
Abstract
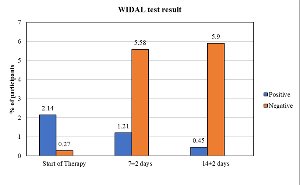
Objective: To evaluate the effectiveness and safety of cefixime for managing typhoid fever among Indian patients. Design: Multicenter, single-arm retrospective study. Patients: Patients with typhoid fever who received cefixime as part of routine clinical practice. Methods: The study retrospectively assessed the data from January 2023 to April 2024. Patient demographics data and clinical evaluation was collected at baseline. At end-of-therapy (7±2 days) and follow-up period (14±2 days), assessment included clinical outcome, persisting symptoms, laboratory tests, and adverse event incidences. Results: Interim data of 6274 patients were retrospectively assessed. Most patients 4,446 (70.9%) presented with a single symptom, while 1761 (28.1%) patients presented with a combination of the symptoms. The WIDAL test at the initiation of the therapy reported 134 (2.14%) positive cases, reducing to 76 (1.21%) at 7±2 days and 28 (0.45%) at 14±2 days follow-up. The average duration of cefixime therapy was 8.21 (3.68) days, with a mean duration of hospital stay of 7.60 (3.84) days. A majority of patients demonstrated clinical cure (96.68%) at 7±2 days, which increased to 99.35% at 14±2 days. Incidence of adverse events was rare, with 6 (0.09%) and 4 (0.06%) documented cases at 7±2 days and 14±2 days, respectively. Conclusion: Cefixime demonstrated high effectiveness and a favourable safety profile among Indian patients with typhoid fever.
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.details##
Copyright (c) 2025 Parikh K, Dinkar JK, Pal A., Pawar D, Sharma A.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Creative Commons License All articles published in Annals of Medicine and Medical Sciences are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Parikh K, Parikh Nursing Home, Mumbai, India.
Dr. Kamlesh Parikh; Parikh Nursing Home, Mumbai, India.
Dinkar JK, Department of General Medicine, Indira Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences, Patna, India.
Dr. Jyoti Kumar Dinkar; Department of General Medicine, Indira Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences, Patna, India.
Pal A., Medical Affairs Department, Alkem Laboratories Ltd., Mumbai, India.
Dr. Amitrajit Pal; Medical Affairs Department, Alkem Laboratories Ltd., Mumbai, India.
Pawar D, Medical Affairs Department, Alkem Laboratories Ltd., Mumbai, India.
Dr. Dattatray Pawar; Medical Affairs Department, Alkem Laboratories Ltd., Mumbai, India.
Sharma A., Medical Affairs Department, Alkem Laboratories Ltd., Mumbai, India.
Dr. Akhilesh Sharma; Medical Affairs Department, Alkem Laboratories Ltd., Mumbai, India.
[1] Barnett R. Typhoid fever. The Lancet. 2016 Nov;388(10059):2467.
[2] Coats J. Eberth’s Typhoid Bacillus. BMJ. 1882 Mar 25;1(1108):421-421.
[3] Parry CM, Qamar FN, Rijal S, McCann N, Baker S, Basnyat B. What Should We Be Recommending for the Treatment of Enteric Fever? Open Forum Infectious Diseases. 2023 Jun 2;10(Supplement_1): S26-31.
[4] Chaudhary MK, Rayamajhi BS, Paudel K, Bajracharya P, Chaudhary RS, Gyawali S. Efficacy of Cefixime in the Treatment of Typhoid Fever. 2013.
[5] Cahuayme-Zuniga L, Malani PN. What Is Typhoid Fever? JAMA [Internet]. 2025 May 8 [cited 2025 Jun 16]; Available from: https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2833763.
[6] Crump JA, Sjölund-Karlsson M, Gordon MA, Parry CM. Epidemiology, Clinical Presentation, Laboratory Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Antimicrobial Management of Invasive Salmonella Infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2015 Oct;28(4):901-37.
[7] Marchello CS, Birkhold M, Crump JA. Complications and mortality of typhoid fever: A global systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Infection. 2020 Dec;81(6):902-10.
[8] Vanderslott S, Phillips MT, Pitzer VE, Kirchhelle C. Water and Filth: Reevaluating the First Era of Sanitary Typhoid Intervention (1840-1940). Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2019 Oct 15;69(Supplement_5): S377-84.
[9] Cutler D, Miller G. The role of public health improvements in health advances: The twentieth-century United States. Demography. 2005 Feb 1;42(1):1-22.
[10] Masuet-Aumatell C, Atouguia J. Typhoid fever infection - Antibiotic resistance and vaccination strategies: A narrative review. Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2021 Mar; 40:101946.
[11] John J, Bavdekar A, Rongsen-Chandola T, Dutta S, Gupta M, Kanungo S, et al. Burden of Typhoid and Paratyphoid Fever in India. N Engl J Med. 2023 Apr 20;388(16):1491-500.
[12] Ochiai RL. a study of typhoid fever in five Asian countries: disease burden and implications for controls. Bull World Health Organ. 2008 Apr 1;86(4):260-8.
[13] Giri A, Karkey A, Dongol S, Arjyal A, Maharjan A, Veeraraghavan B, et al. Azithromycin and cefixime combination versus azithromycin alone for the out-patient treatment of clinically suspected or confirmed uncomplicated typhoid fever in South Asia: a randomised controlled trial protocol [version 2; peer review: 2 approved]. Wellcome Open Research. 2021.
[14] Veeraraghavan B, Pragasam AK, Bakthavatchalam YD, Ralph R. Typhoid Fever: Issues in Laboratory Detection, Treatment Options & Concerns in Management in Developing Countries. Future Sci OA. 2018 Jul;4(6): FSO312.
[15] Pustake M, Giri P, Tambolkar S, Nayak S. Extensively Drug-Resistant Typhoid Fever: A Call to Action. Indian Journal of Community Medicine. 2022 Jan;47(1):153-4.
[16] Khadka P, Thapaliya J, Thapa S. Susceptibility pattern of Salmonella enterica against commonly prescribed antibiotics, to febrile-pediatric cases, in low-income countries. BMC Pediatr. 2021 Dec;21(1):38.
[17] Ramdhani D, Kusuma SAF, Sediana D, Bima APH, Khumairoh I. Comparative study of cefixime and tetracycline as an evaluation policy driven by the antibiotic resistance crisis in Indonesia. Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 16;11(1):18461.
[18] Nassar H, Sippl W, Dahab RA, Taha M. Molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations and in vitro screening reveal cefixime and ceftriaxone as GSK3β covalent inhibitors. RSC Adv. 2023;13(17):11278-90.
[19] Ray B, Raha A. Typhoid and Enteric Fevers in Intensive Care Unit. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2021 May;25(Suppl 2): S144-9.
[20] Mishra C, Jha AK, Ahmad MdP, Singh S, Ansari AA. A Comparative Study Between Cefixime and Ofloxacin in The Treatment of Uncomplicated Typhoid Fever Attending A Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital. Med Phoenix. 2017 Oct 13;2(1):3-7.
[21] Bhargava M, Chandra C. ANALYSIS OF CEFIXIME IN THE MANAGEMENT OF TYPHOID FEVER: A CLINICAL STUDY. Journal of Advanced Medical and Dental Sciences Research. 2016;4(6).
[22] Mohammed TY, El-Tawab HA, El-Moktader AA. Efficacy and Safety of Oral Cefixime for the Short-Term Treatment of Typhoid Fever in a Group of Egyptian Children.
[23] Thapa RK, Shrestha S. Comparative Study of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Azithromycin and Cefixime against Salmonella Typhi Infection. J Manmohan Memorial Inst Health Sci. 2020 Aug 7;6(1):67-80.
[24] Vinh H, Wain J, Vo TN, Cao NN, Mai TC, Bethell D, et al. Two or three days of ofloxacin treatment for uncomplicated multidrug-resistant typhoid fever in children. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1996 Apr;40(4):958-61.
[25] Girgis NI, Kilpatrick ME, Farid Z, Sultan Y, Podgore JK. Cefixime in the treatment of enteric fever in children. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1993;19(1):47-9.
[26] Matsumoto Y, Ikemoto A, Tawara S. Antibacterial activity of cefixime against Salmonella typhi and applicability of Etest. J Infect Chemother. 1999;5:176-9.
[27] Bhutta ZA, Khan IA, Molla AM. Therapy of multidrug-resistant typhoid fever with oral cefixime vs. intravenous ceftriaxone: The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal. 1994 Nov;13(11):990-3.
[28] Lin X, Kück U. Cephalosporins as key lead generation beta-lactam antibiotics. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Dec;106(24):8007-20.
[29] Khadka S, Shrestha B, Pokhrel A, Khadka S, Joshi RD, Banjara MR. Antimicrobial Resistance in Salmonella Typhi Isolated from a Referral Hospital of Kathmandu, Nepal. Microbiol�Insights. 2021 Jan;14:11786361211056350.
[30] Girgis NI, Tribble DR, Sultan Y, Farid Z. Short Course Chemotherapy with Cefixime in Children with Multidrug-resistant Salmonella typhi Septicaemia. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics. 1995 Dec 1;41(6):364-5.
[31] Shigi Y, Matsumoto Y, Kaizu M, Fujishita Y, Kojo H. Mechanism of action of the new orally active cephalosporin FK027. J Antibiot. 1984;37(7):790-6.
[32] Alsoub H, Uwaydah AK, Matar I, Zebeib M, Elhag KM. A clinical comparison of typhoid fever caused by susceptible and multidrug-resistant strains of Salmonella typhi. Br J Clin Pract. 1997;51(1):8-10.
[33] Ujjan RA, Shaikh GS, Pathan S, Niamat M, Shaikh F, Ali K. The Effectiveness of Azithromycin versus Cefixime in the Treatment of Typhoid Fever in Children: Azithromycin versus Cefixime in the Treatment of Typhoid Fever. PJHS-Lahore. 2024 Oct 31;179-83.
[34] Amin MR, Das SK, Kabir A, Islam MR, Ahmed SM, Hasan MJ. Open Label Randomized Controlled Comparison of Three Alternative Regimes of Ciprofloxacin, Azithromycin and Cefixime for Treatment of Uncomplicated Typhoid Fever in Bangladesh. Mymensingh Med J. 2021 Jul;30(3):725-37.
[35] Sandman Z, Iqbal O. Azithromycin. In StatPearls [Internet]; 2023.
[36] Kuehn R, Stoesser N, Eyre D, Darton TC, Basnyat B, Parry CM. Treatment of enteric fever (typhoid and paratyphoid fever) with cephalosporins. Cochrane Infectious Diseases Group, editor. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews [Internet]. 2022 Nov 24 [cited 2025 Jun 19];2022(11). Available from: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/14651858.CD010452.pub2
[37] Jonville-Béra AP, Largeau B, Di Meglio F, Pariente A. The safety profile of fluoroquinolones. Infectious Diseases Now. 2025 Jun;55(4):105064.
[38] Tally FP, Desjardins RE, Mccarthy EF, Cartwright K. Safety profile of cefixime: The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal. 1987 Oct;6(10):976-80.
[39] Mohsen S, Dickinson JA, Somayaji R. Update on the adverse effects of antimicrobial therapies in community practice. Can Fam Physician. 2020 Sep;66(9):e228-37.
[40] Dragostin I, Dragostin OM, Lisă EL, Stefan SC, Zamfir AS, Diaconu C, et al. Drugs frequently involved in inducing hypersensitivity reactions. Drug and Chemical Toxicology. 2022 Mar 4;45(2):617-24.