PFN A3 in Intertrochanteric Fractures: A Game Changer in Proximal Femoral Fixation
Authors
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.main##
Abstract
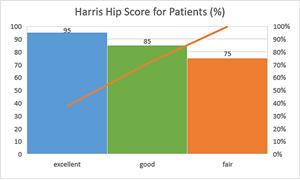
Background: Intertrochanteric fractures, unstable particularly (AO/OTA 31-A3), is difficult to treat. Proximal femoral nailing (PFN) has emerged as a convenient means of its treatment owing to biomechanical superiority to achieve optimal stability and minimizing complications, particularly comminuted or osteoporotic fractures. This article explores the effectiveness of a PFN A3 design in the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures. To assess the clinical and radiologic results of the use of the PFN A3 for fixation of intertrochanteric fractures, particularly in the stability of fixation, fracture union, and complication reduction. Material & Methods: In this retrospective analysis, 158 patients (48 men, 110 women; age range, 47-95 years) who had surgical fixation with the PFN A3 for intertrochanteric fractures from September 2022 to April 2025 were studied. Seventy-five fractures were on the right side and 83 on the left side. Fracture classification, operative time, blood loss, union rate, time to weight-bearing, and complications were recorded and compared. Results: The mean age of the study population was 78.3 years, with a slight female predominance (69.62%). The distribution of Modified Harris Hip Score (MHHS) among study participants revealed significant variations with age, while differences based on sex and AO/OTA classification were not statistically significant, with 26% of patients categorized as having good outcomes and 36% classified as excellent. Younger patients demonstrated significantly better functional outcomes. The mean neck–shaft angle was 137°, with no significant variation across demographic groups. The mean TAD was 21.09 mm. Post-operative complications were minimal, with screw cut-out occurred in no cases and superficial wound healing delays in 0.17%, sepsis in 1.26%. Conclusion: For intertrochanteric fractures PFN A3 implant plays a significant role as far as femoral fixation especially in older individuals due to the osteoporotic nature of the bone in elderly patients.
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.details##
Copyright (c) 2025 Vinay Kumar, Sajjad Ali, Dibin DK, Mohammed Irshad P M, Mohamed Nafsal Velakadu Navasali, Peeyush Rawat, Jamila Hameed

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Creative Commons License All articles published in Annals of Medicine and Medical Sciences are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Vinay Kumar, Faculty of Department of Orthopaedics, Karuna Medical College, Vilayodi, Chittur, Palakkad, Kerala, 678103, India.
Faculty of Department of Orthopaedics, Karuna Medical College, Vilayodi, Chittur, Palakkad, Kerala, 678103, India.
Sajjad Ali, Faculty of Department of Orthopaedics, Karuna Medical College, Vilayodi, Chittur, Palakkad, Kerala, 678103, India.
Faculty of Department of Orthopaedics, Karuna Medical College, Vilayodi, Chittur, Palakkad, Kerala, 678103, India.
Dibin DK, Faculty of Department of Orthopaedics, Karuna Medical College, Vilayodi, Chittur, Palakkad, Kerala, 678103, India.
Faculty of Department of Orthopaedics, Karuna Medical College, Vilayodi, Chittur, Palakkad, Kerala, 678103, India.
Mohammed Irshad P M, Faculty of Department of Orthopaedics, Karuna Medical College, Vilayodi, Chittur, Palakkad, Kerala, 678103, India.
Faculty of Department of Orthopaedics, Karuna Medical College, Vilayodi, Chittur, Palakkad, Kerala, 678103, India.
Mohamed Nafsal Velakadu Navasali, CRMI, Karuna Medical College Hospital, Vilayodi, Palakkad, Kerala, 678103, India.
CRMI, Karuna Medical College Hospital, Vilayodi, Palakkad, Kerala, 678103, India.
Peeyush Rawat, CRMI, Karuna Medical College Hospital, Vilayodi, Palakkad, Kerala, 678103, India.
CRMI, Karuna Medical College Hospital, Vilayodi, Palakkad, Kerala, 678103, India.
Jamila Hameed, Research Mentor, Karuna Medical College, Vilayodi, Chittur, Palakkad, Kerala, 678103, India.
Research Mentor, Karuna Medical College, Vilayodi, Chittur, Palakkad, Kerala, 678103, India.
[1] Kumar P, Rajnish RK, Sharma S, Dhillon MS. Proximal femoral nailing is superior to hemiarthroplasty in AO/OTA A2 and A3 intertrochanteric femur fractures in the elderly: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Int Orthop. 2020;44(4):623-633. doi:10.1007/s00264-019-04351-9
[2] Amer KM, Congiusta DV, Jain K, et al. Complication Rates in Intertrochanteric Fractures: A Database Analysis Comparing Sliding Hip Screw and Cephalomedullary Nail. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2024;12(7):506-514. doi:10.22038/ABJS.2024.64188.3081
[3] Guo T, Zhang F, Xiong L, et al. Association of Handgrip Strength with Hip Fracture and Falls in Community-dwelling Middle-aged and Older Adults: A 4-Year Longitudinal Study. Orthop Surg. 2024;16(5):1051-1063. doi:10.1111/os.14029
[4] Polat G, Bayram S, Gökçeoğlu YS, Albayrak O, Kahraman A, Durmaz H. The Effect of Bone Morphology on Fracture Type and Treatment Result in Patients with Intertrochanteric Femur Fracture Aged over 65 year. 65 Yaş Üstü İntertrokanterik Femur Kırığı Hastalarında Kemik Morfolojisinin Kırık Tipine ve Tedavi Sonucuna Etkisi. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2022;28(12):1731-1738. doi:10.14744/tjtes.2022.57400
[5] Rathbun AM, Shardell M, Orwig D, Hebel JR, Hicks GE, Beck TJ, et al. Difference in the trajectory of change in bone geometry as measured by hip structural analysis in the narrow neck, intertrochanteric region, and femoral shaft between men and women following hip fracture. Bone 2016;92:124-31.
[6] Müller ME, Nazarian S, Koch P, Schatzker J. The Comprehensive Classification of Fractures of Long Bones. Berlin, Germany: Springer-Verlag; 1990.
[7] Nasim O, Kohli S, Eskander B, Girgis S, Kent M. Periprosthetic Fractures in Long Versus Short Proximal Femoral Nailing for Intertrochanteric Fractures: A 10-Year Single-Centre Cohort Study. Cureus. 2022;14(12):e32892. Published 2022 Dec 23. doi:10.7759/cureus.32892
[8] Şensöz E, Ergun S, Kayaalp ME, Eceviz E. The Comparison of Dynamic Condylar Screw Plate to Proximal Femoral Nail in Reverse Oblique and Transverse Intertrochanteric Fractures: A Retrospective Study on 61 Patients. Cureus. 2023;15(3):e36397. Published 2023 Mar 20. doi:10.7759/cureus.36397
[9] Gadegone WM, Shivashankar B, Lokhande V, Salphale Y. Augmentation of proximal femoral nail in unstable trochanteric fractures. SICOT J. 2017;3:12. doi:10.1051/sicotj/2016052
[10] Bhardwaj S, Sakale H, Agrawal AC, et al. A Comparison of the Clinicoradiological Outcomes of Intertrochanteric Fractures Treated Using Proximal Femoral Nail and Proximal Femoral Nail Anti-rotation. Cureus. 2024;16(5):e60639. Published 2024 May 19. doi:10.7759/cureus.60639
[11] Murugan PB, Mohideen S, Pradeep E, Kumar KVA, Pandian H, Ashwin VY. Comparison of functional and radiological outcome of unstable intertrochanteric femur fractures treated using PFN and PFNA in patients with osteoporosis. J Orthop Case Rep. 2024;14(10):219-224. doi:10.13107/jocr.2024.v14.i10.4870
[12] Solunke S, Nair A, Agrawal R, Deshmukh A, Barosani A. Prospective Research Comparing Different Trochanteric Fracture Fixation Techniques. Cureus. 2024;16(8):e67774. Published 2024 Aug 25. doi:10.7759/cureus.67774
[13] Harold RE, Butler BA, Delagrammaticas D, Sullivan R, Stover M, Manning DW. Patient-reported outcomes measurement information system correlates with modified harris hip score in total hip arthroplasty. Orthopedics 2020;44:e19-25.
[14] Sharma A, Mahajan A, John B. A Comparison of the Clinico-Radiological Outcomes with Proximal Femoral Nail (PFN) and Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA) in Fixation of Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017;11(7):RC05-RC09. doi:10.7860/JCDR/2017/28492.10181
[15] K Rahman MA, Siddiqui YS, Julfiqar M, Khan AQ, Sabir AB, Abbas M. Short versus long proximal femoral nail in the management of intertrochanteric fractures - a comparative study. Int J Burns Trauma. 2023;13(3):99-109. Published 2023 Jun 15.
[16] Adeel K, Nadeem RD, Akhtar M, Sah RK, Mohy-Ud-Din I. Comparison of proximal femoral nail (PFN) and dynamic hip screw (DHS) for the treatment of AO type A2 and A3 pertrochanteric fractures of femur. J Pak Med Assoc. 2020;70(5):815-819. doi:10.5455/JPMA.295426
[17] Yu F, Tang YW, Wang J, Lin ZC, Liu YB. Does intramedullary nail have advantages over dynamic hip screw for the treatment of AO/OTA31A1-A3? A meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):588. Published 2023 Jul 18. doi:10.1186/s12891-023-06715-0
[18] Walton MJ, Barnett AJ, Jackson M. Tip-Apex Distance as a Predictor of Failure Following Cephalo-Medullary Fixation for Unstable Fractures of the Proximal Femur. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2008;34(3):273-276. doi:10.1007/s00068-008-7075-3
[19] Jain R, Chhawra S, Karnati AR, Nagar AK, Anand R. Technical Note in Case Series a Novel Recent Technique for the Removal of Broken PFNA-II Blade in Intertrochanteric Fractures is a Technical Challenge. J Orthop Case Rep. 2024;14(11):246-250. doi:10.13107/jocr.2024.v14.i11.4982
[20] FeldinszkÁ J, Jacko P, Barinka J, Kilian M, Šimko P. Porovnanie dvojskrutkového implantátu a antirotačnej čepele pri liečbe trochanterických zlomenín femuru [Comparison of 2-Screw Implant and Antirotational Blade Implant in Treatment of Trochanteric Fractures]. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2020;87(4):268-272.
[21] Menezes DF, Gamulin A, Noesberger B. Is the proximal femoral nail a suitable implant for treatment of all trochanteric fractures? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005; 439:221-227.